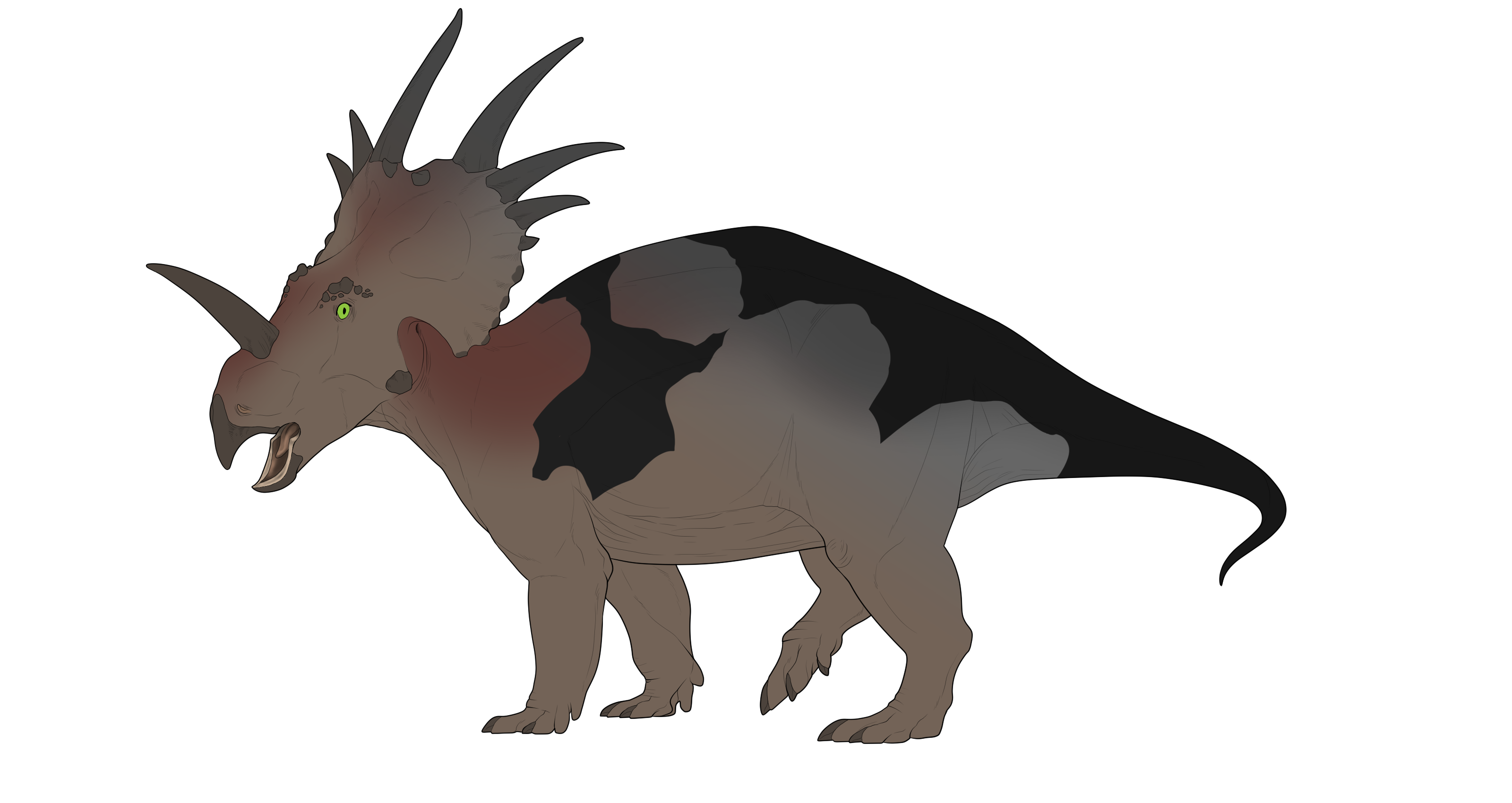
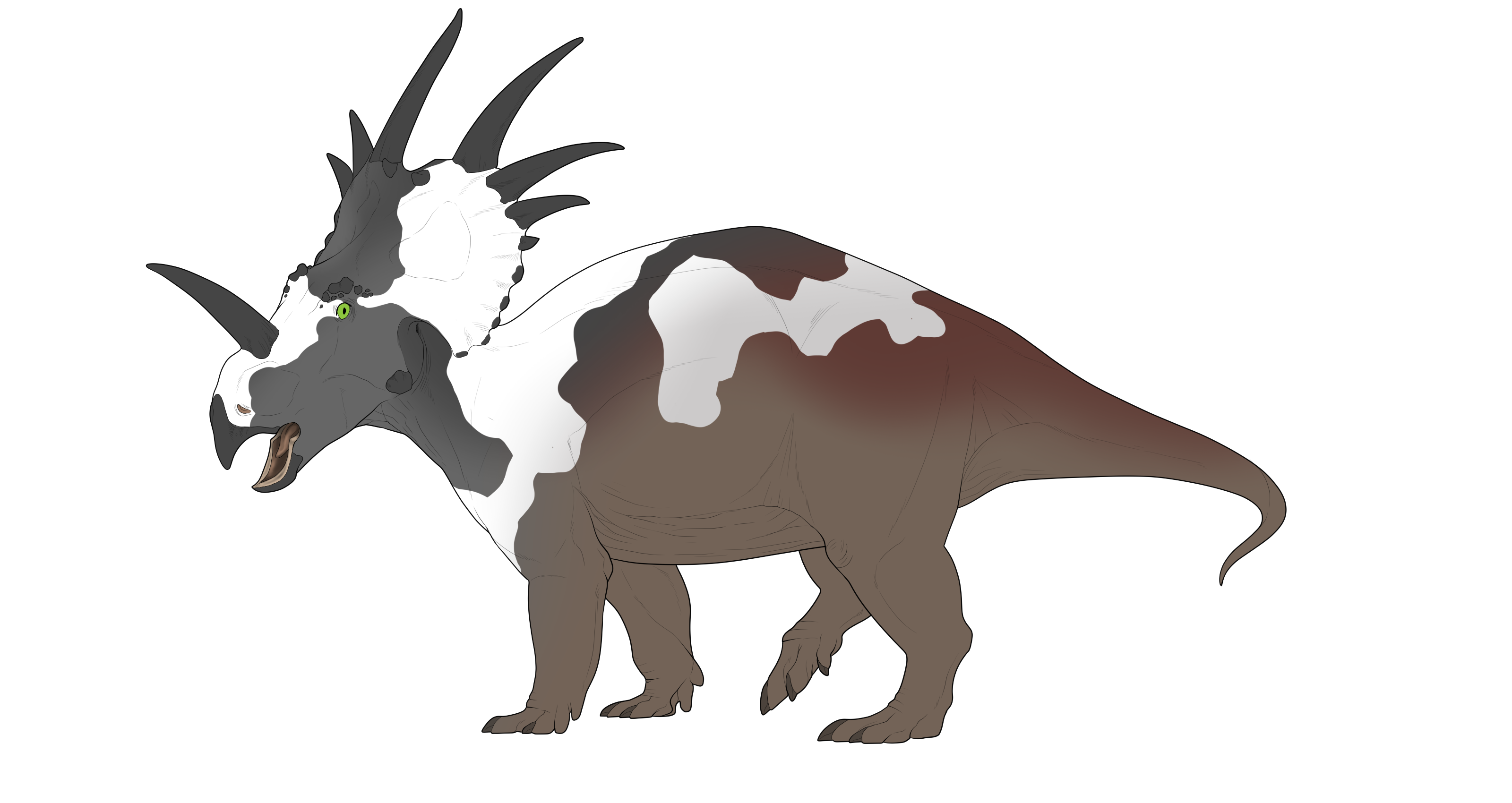
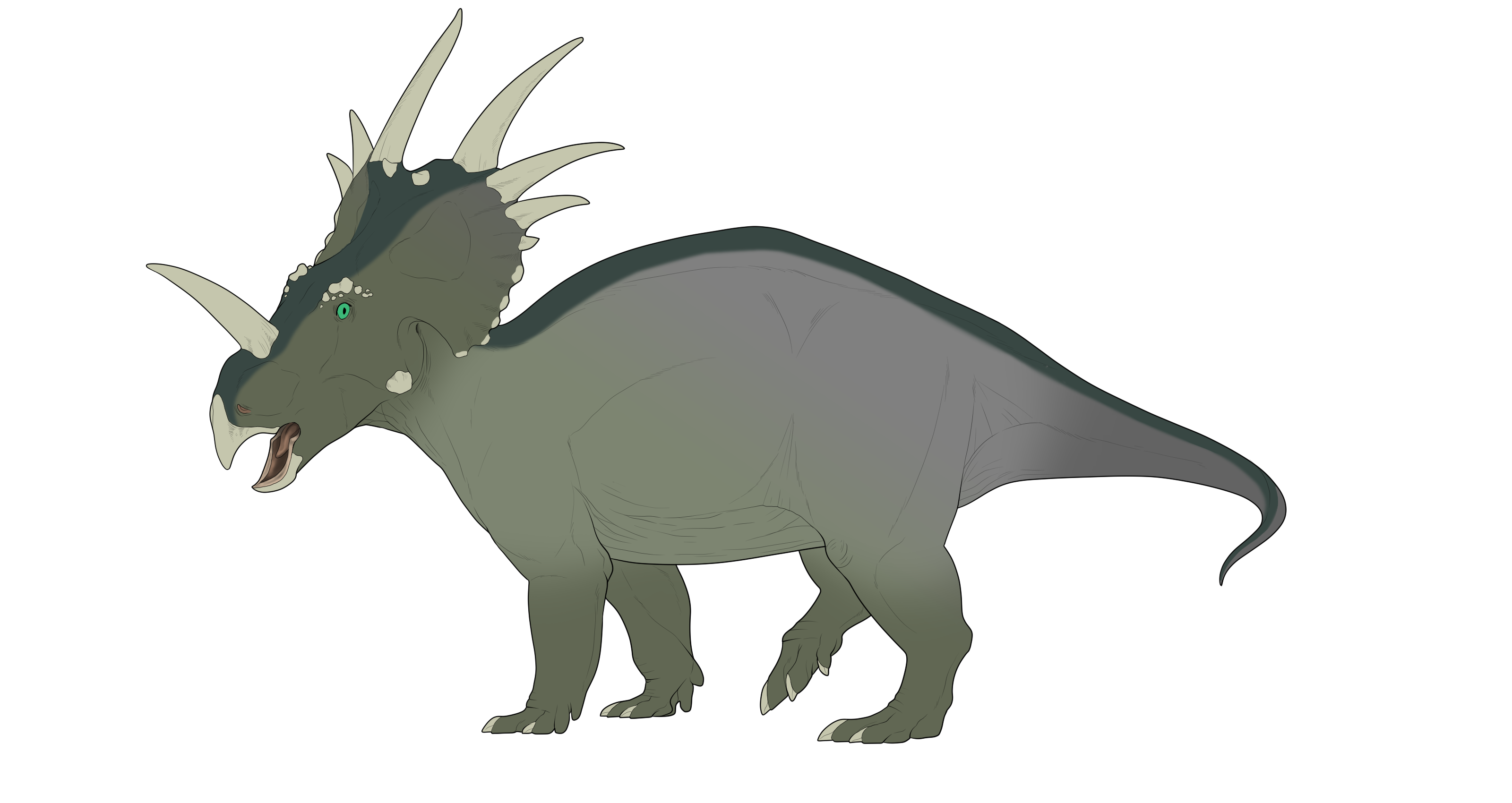
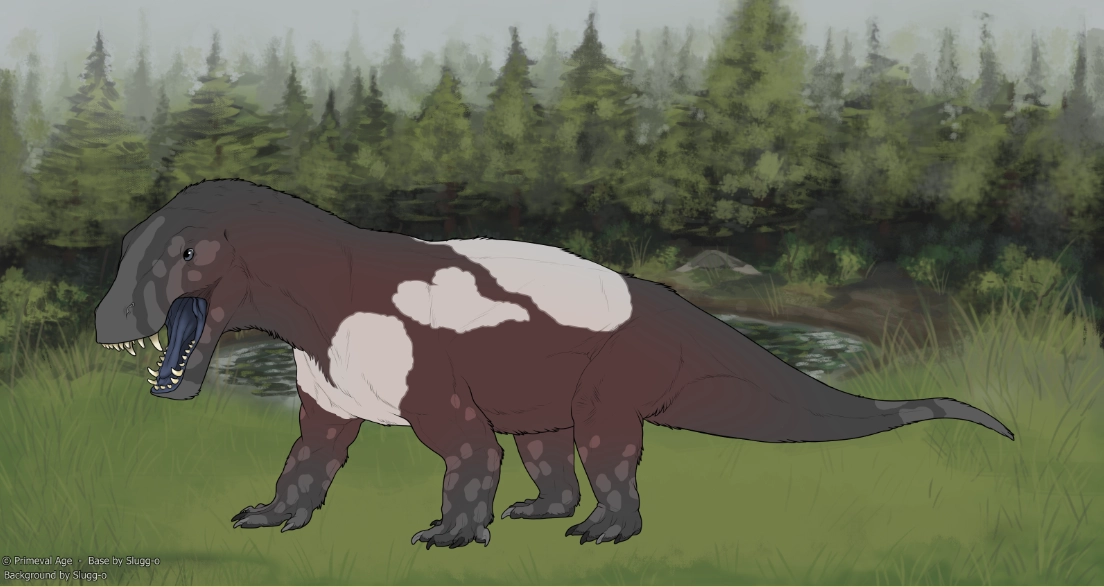
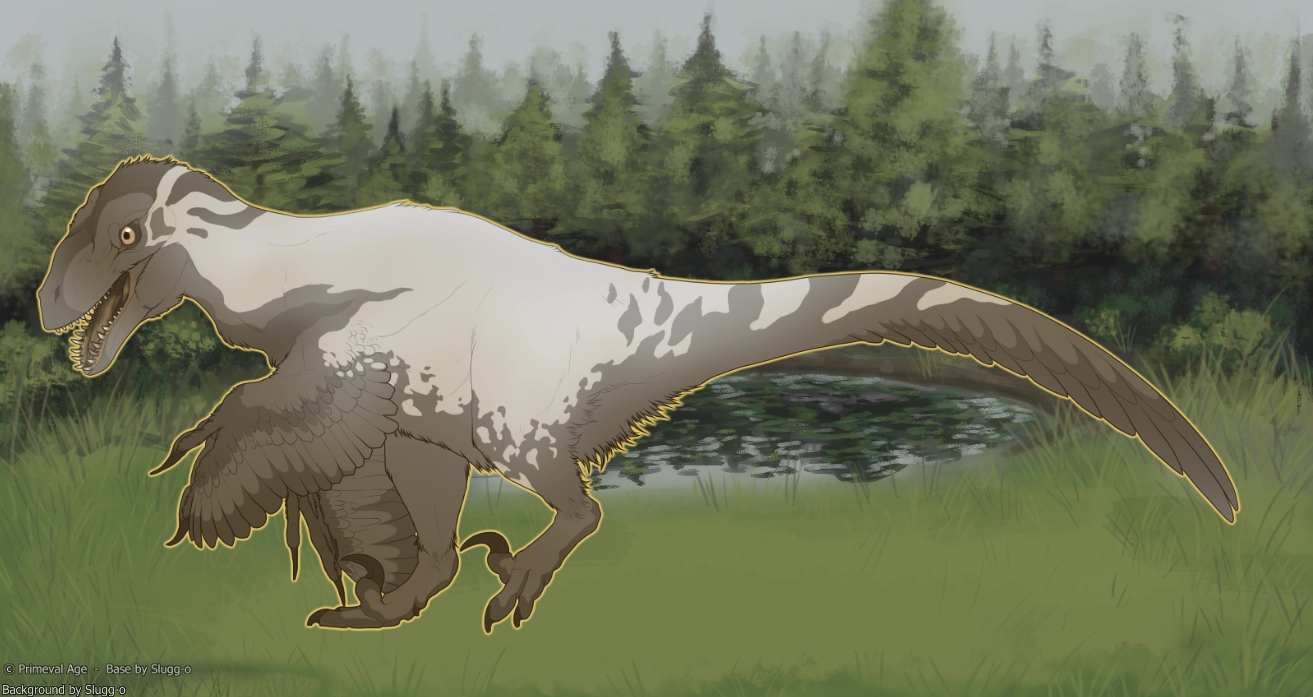
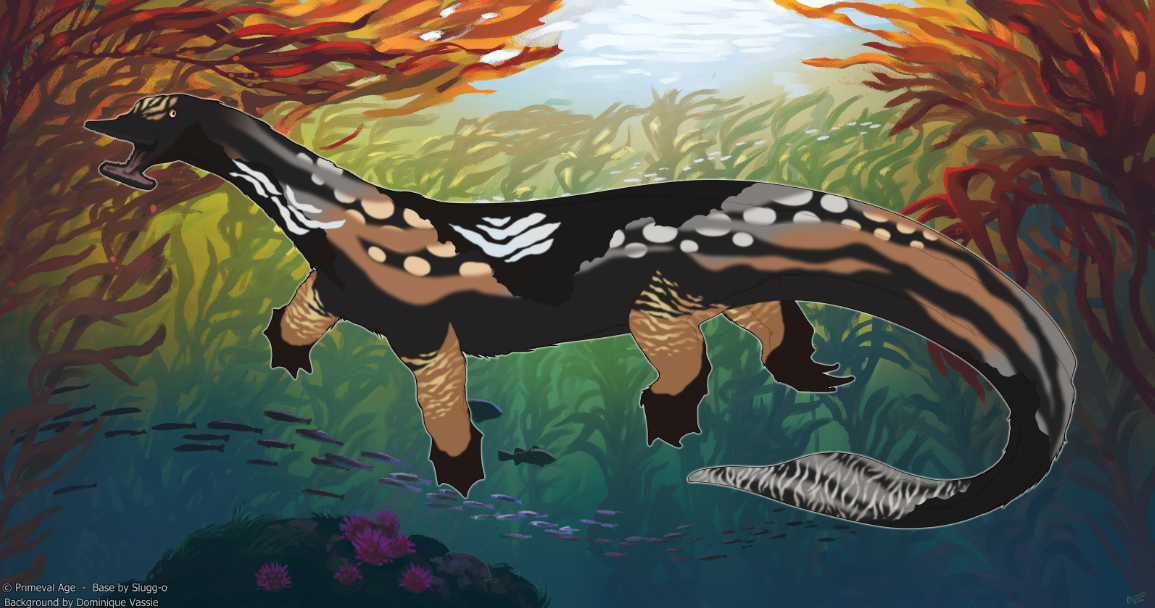
xGSGrayscale is a mutation that grays out areas of the body
Skip to:
Skip to:
- Shape and Placement - Color - Interactions - Edge Types - Examples - Ranges -
Shape and Placement
- Acts as a modifier by causing everything in the affected areas to turn gray - not a separate marking on top.
- Grayscale cannot form small or intricate shapes.
- Can mimic normal markings, but is not allowed to mimic other mutations.
Color
Interactions
- Must layer above all other markings, including markings such as Curse and Piebald, and dimorphic markings.
-- An additional version of your import to show dimorphics unaffected by grayscale is recommended, but not required! - May layer on top of or under other mutations as long as its consistent across the design.
-- Can present on other mutation features. - Eyes touching grayscale can present sectoral heterochromia.
- Can affect keratin.
- Overrides color modifiers. If grayscale and a color modifier are present in the same area, grayscale layers on top and turns the area gray.
Allowed Edge Types
Grayscale is allowed one edge type from the below options - a guide to each edge type can be found by clicking on the images
Examples
Correct Examples
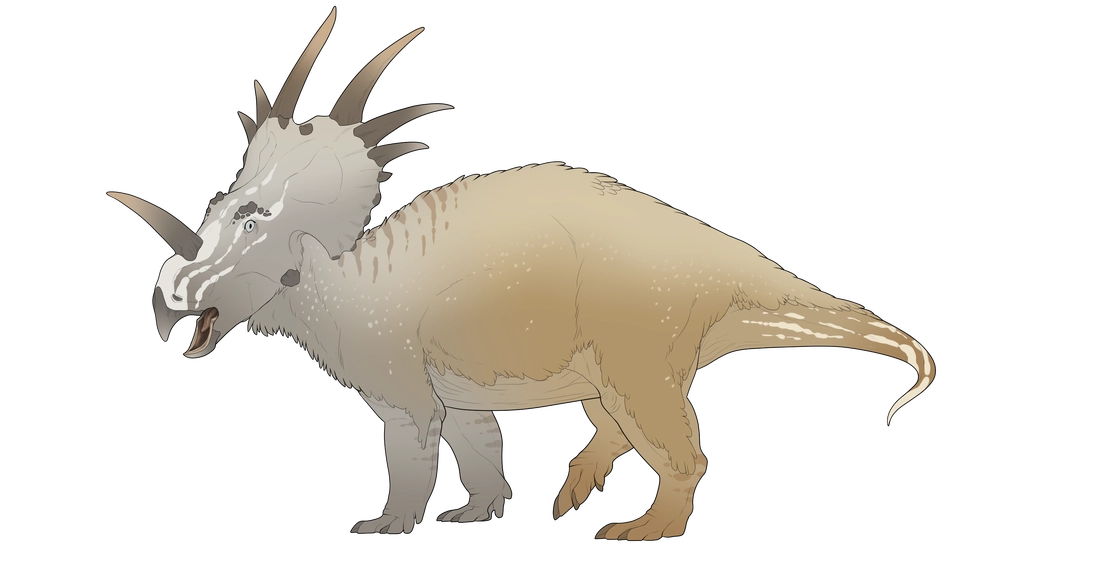

Incorrect Examples
Correct Imports
Incorrect Imports

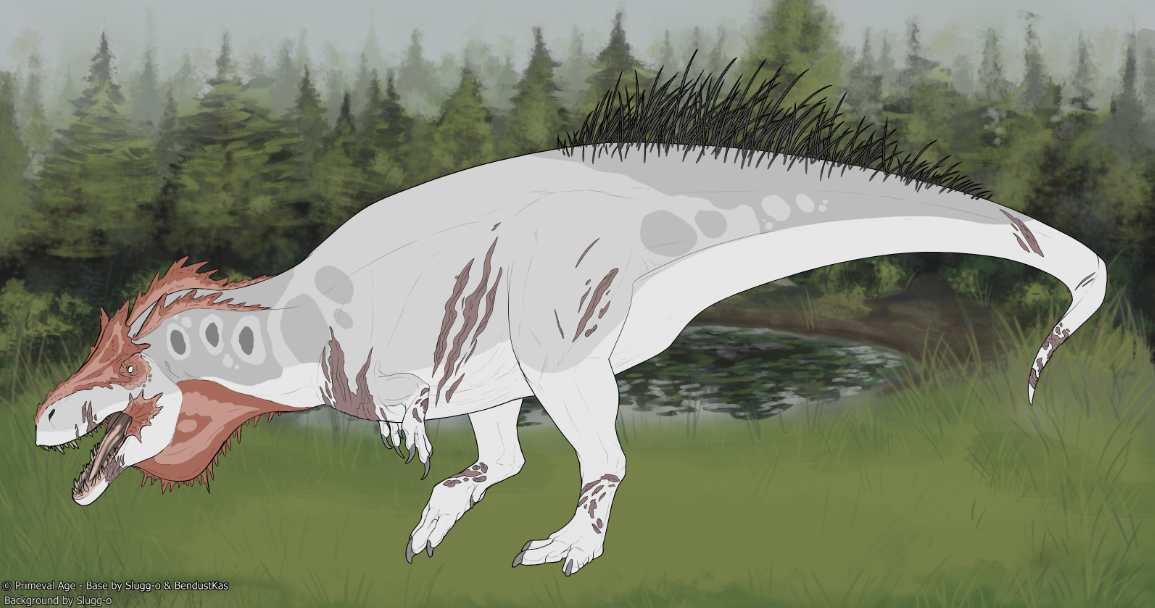
Grayscale presenting as one large area on the front of the body and affecting keratin and the dimorphic marking.
No examples yet!
Range
- Minimum requirement - at least 10% coverage.
- Maximum allowance - can cover up to 100% of the body.
- This mutation may present anywhere on the body but can not affect the mouth or teeth.
-- Can be in separate areas of the body - does not need to all be in one area.